Recently, a stress-relieving artifact-Fidget Spinner (which is also named as Finger Spinner) - sweeps the world. It is a small toy with a symmetric bearing system that can spin on one’s finger, and it is said that this toy can be used to help treat ADHD, relieve anxiety, reduce stress, give up smoking, pass the time, etc.
 From
the beginning of 2016, this little spinning top was being popular slowly in
North America, and now it has been all the rage in the INS friends circle. In
the most famous video website of the world, YouTube, the total hits of video
about fidget spinners have already exceeded 100 million. The fidget spinner is
so hot that it leads to a ripple effect. In China, factories enthusiastically
follow the latest fashion and increase production without regard to the cost.
From
the beginning of 2016, this little spinning top was being popular slowly in
North America, and now it has been all the rage in the INS friends circle. In
the most famous video website of the world, YouTube, the total hits of video
about fidget spinners have already exceeded 100 million. The fidget spinner is
so hot that it leads to a ripple effect. In China, factories enthusiastically
follow the latest fashion and increase production without regard to the cost.
However, as a professional 3rd-party testing laboratory, C&K Testing must remind you: as the fidget spinner belongs to toys, it has to meet relevant technical regulations or standards before its domestic sale or export, or it may encounter disposal measures like punishing, withdrawing or even destroying.
| Product Analysis
The fidget spinners on the markets have various types, including triangular model (with rounded edges), wheel-like model, three-bladed model and two-bladed model, and they can also be divided into the categories of luminous and nonluminous.
Take the most common triangular fidget spinner with rounded edges as an example. These little toys generally consist of 3 main structures, which are removable cap, shell and bearing, and luminous fidget spinner also contains a LED luminescent module, which includes button cells, PCB layout, electrical components, solder joints, metal connection terminals, springs and other components.
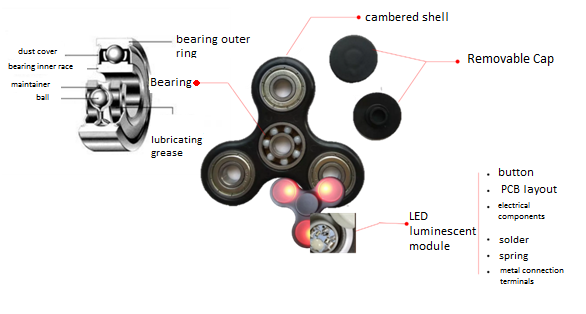
| Analysis on the Risk Control Point of Products
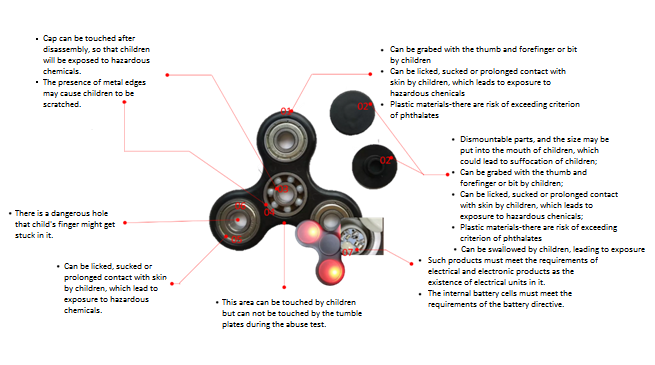
| Recommended Test Scheme
Target market → Product Component↓ | China | EU | America | |||
Test projects | Project basis | Test projects | Project basis | Test projects | Project basis | |
The entire product | Drop test | GB 6675.2 | Drop test | EN 71-1 | Drop test | ASTM F963 |
Tensile test | GB 6675.2 | Tensile test | EN 71-1 | Tensile test | ASTM F963 | |
Torque test | GB 6675.2 | Torque test | EN 71-1 | Torque test | ASTM F963 | |
Pressure test | GB 6675.2 | Pressure test | EN 71-1 | Pressure test | ASTM F963 | |
01 Plastic shell | Soluble heavy metal | GB 6675.4 | Soluble heavy metal | Toy Safety Directive /EN 71-3 | Soluble heavy metal | ASTM F963 |
Phthalate | GB 6675.1 | Phthalate | REACH Regulation | Phthalate | CPSIA | |
total lead | CPSIA | |||||
02 Demountable plastic cap | Tiny parts | GB 6675.2 | Tiny parts | EN 71-1 | Tiny parts | ASTM F963 |
Soluble heavy metal | GB 6675.4 | Soluble heavy metal | Toy Safety Directive /EN 71-3 | Soluble heavy metal | ASTM F963 | |
Phthalate | GB 6675.1 | Phthalate | REACH Regulation | Phthalate | CPSIA | |
Total lead | CPSIA | |||||
03 Inner ring of the metal bearing | Sharp edges | GB 6675.2 | Sharp edges | EN 71-1 | Sharp edges | ASTM F963 |
Soluble heavy metal | GB 6675.4 | Soluble heavy metal | Toy Safety Directive /EN 71-3 | Soluble heavy metal | ASTM F963 | |
Total lead | CPSIA | |||||
04outer ring of the metal bearing | Sharp edges | GB 6675.2 | Sharp edges | EN 71-1 | Sharp edges | ASTM F963 |
Soluble heavy metal | GB 6675.4 | Soluble heavy metal | Toy Safety Directive /EN 71-3 | Soluble heavy metal | ASTM F963 | |
Total Lead | CPSIA | |||||
05 metal sealing ring of the bearing | Soluble heavy metal | GB 6675.4 | Soluble heavy metal | Toy Safety Directive /EN 71-3 | Soluble heavy metal | ASTM F963 |
Total lead | CPSIA | |||||
06The round hole | Accessibility test | GB6675.2 | Accessibility test | EN 71-1 | Accessibility test | ASTM F963 |
* The items listed above are not the final test scheme but for reference only.
As for those fidget spinners that can glow, they should not only meet the above requirements but also Measures for the Administration of Restricted Use of Hazardous Substances Contained in Electrical and Electronic Products, Electric toy-Safety GB 19865, EU RoHS 2 Directive (2011/65/EU), Electric Toys Standard EN 62115, EU Battery Directive 2006/66/EC, the requirement to battery-powered toys under ASTM F963, etc.
The test schemes that we design for each product will be different for their difference on aspects like product structure, material, whether every part of the product are accessible or not, whether it could enter the mouth and the age of applicable children. After taking into account children’s behavior and the abuse testing, some of the inaccessible components may become accessible or mouth-accessible so that they also need to meet the requirement of relevant physical or chemical testing.
C&K Testing reminds that, at the beginning of the product designing, product manufacturers should fully comprehend the requirements of relevant regulations and standards so as to avoid the risk point; as the control of material properties and hazardous substance on children products will be much stricter, it is important to select high-quality suppliers in the procurement of raw materials; products that exported to different countries or regions must first meet the requirements of corresponding regulations and standards. However, these regulations and standards always have difference on projects and restrictions, so it is one of the main methods of product quality control to send the finished product for testing to confirm its compliance
The laboratories of C&K Testing established a management system according to ISO / IEC 17025, with a large number of advanced testing instruments and equipments, including gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS), high performance liquid chromatography, ultraviolet/ infrared spectrophotometer, atomic absorption spectrometer, inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer. C&K Testing has been accredited by China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment (CNAS) and China Metrology Accreditation (CMA), and is also recognized by the US Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) as a 3rd-party testing lab in China, devoting its energies to provide companies with consultation of regulations, analyses on product risk, recommended test scheme, product testing, training of supply chain regulations and other services so as to help companies cross technical barriers to trade.
