The European Commission validated 134 notifications as regards food contact materials in 2016. It is noted that more than 80% products through the Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed (RASFF) notified came from China primarily caused by migration of formaldehyde, aromatic amines and heavy elements (cadmium, cobalt, chromium, manganese, nickel and lead), excessive levels of phthalates.
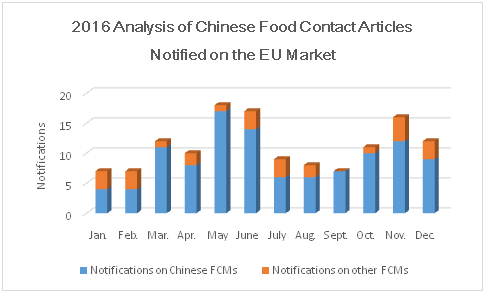
Based on RASFF statistics, EU validated notifications for 2,943 products throughout the year of 2016, including 134 notifications for food contact materials (accounting for 4.55% of the total). But it is noted more than 80% food contact articles notified came from China.
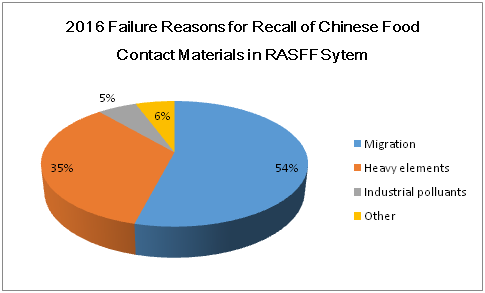
The major reasons for violation includes migration, heavy elements, industrial pollutants and foreign objects, fraud, sensory and other hazards.
Migration: formaldehyde, primary aromatic amines, overall migration and phthalates.
Heavy elements: cadmium, cobalt, chromium, manganese, nickel and lead
Industrial pollutants: tripolycyanamide
Other: fragments, corrosion, lack of declaration of compliance (Doc), etc.
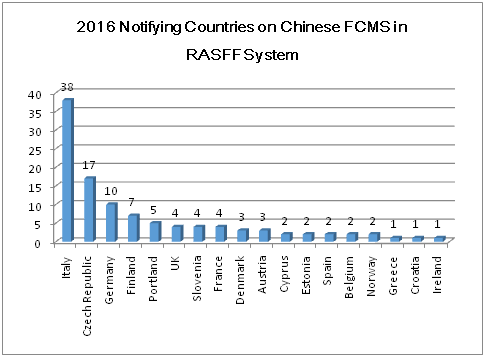
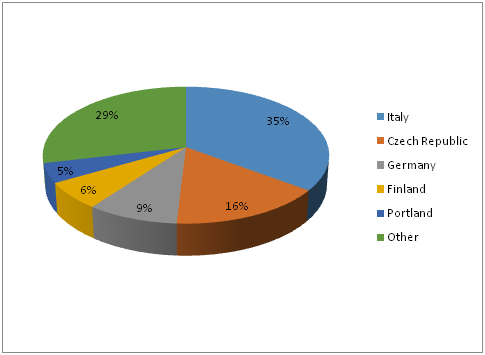
In 2016, 18 EU countries validated notifications on Chinese products through the RASFF system. The five most frequently notifying countries (Italy, Czech Republic, Germany, Finland and Portland) accounted for 71%.
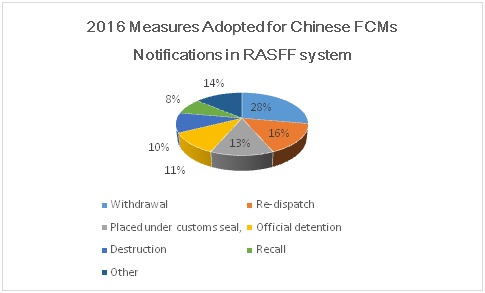
Notifying countries adopts measures such as re-dispatch, withdrawal, placed under customs seal, official detention, destruction and recall.
2016 Regulatory Updates in the Field of Food Contact Materials
On 25 August 2016, EU released Regulation (EU) 2016/1416 to amend Regulation (EU) 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles that intended to come into direct contact with food as regards specific migration limits of heavy metals, union list of authorised substances, test methods for overall and specific migration. More Info
In June 2016, the French General Directorate for Competition Policy, Consumer Affairs and Fraud Control (DGCCRF) published new documents DM/4B/COM/002, DM/4B/COM/003, DM/4B/COM/004 for food contact materials (FCMs) made from inorganic materials (except metals), organic materials made from synthetic fibers and organic materials made from plant fibers. The documents replace the specification in scope of Information Notice No. 2004-64 of 6 May 2004. More Info
In November 2015, DGCCFF, General Directorate for Competition Policy, Consumer Affairs and Fraud Control, published Document DM/4B/COM/001 to pose new requirements on food safety concerning metal and alloy food contact materials (FCMs), which supersede requirements on metal and alloy FCMs in DGCCRF NI No. 2004-64 on 1 January 2016. More Info
Challenges Faced by EU Food Contact Materials Regulatory Compliance in 2017
All plastic food contact materials and articles on the EU market shall comply with Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 since 14 September 2017. The amendments in food simulants, test temperatures and limits require businesses to do new tests.
On 14 March 2016, EU notified World Trade Organisation (WTO) of Circular G/TBT/N/EU/370 to publish a draft Commission Regulation proposing to amend Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 for plastic food contact materials. The amendment targets at regulating the use of bisphenol A (“BPA”) in vanishes and coatings of plastic food contact materials. More Info
The stringent regulation places more severe technical barriers for EU exporters. From the above charts, we can see the strict enforcement on food contact materials, Chinese food contact materials in particular. C&K Testing advises businesses should adjust their manufacturing techniques or materials to ensure product testing.
|Further Information: Recall notifications
|Our Services: Food Contact Materials
